The Importance of Checking Your Moles
Frequency of Moles Examination
Regular Self-Checks:
- It’s crucial for everyone with moles to perform self-examinations at home consistently.
- Ideally, moles should undergo scrutiny every month.
- Incorporating mole checks into a daily routine is beneficial, like examining them post-shower or bath.
Indications for Professional Evaluation
Determining Factors:
- Certain individuals may require professional mole assessments for various reasons, especially if they are at a heightened risk of skin cancer.
- Fair-haired, fair-eyed, or pale-skinned individuals prone to sunburn.
- Those with numerous freckles or a history of sunbed use.
- Individuals with a high count of moles (100+) or large moles (>6mm).
- Those with a personal or family history of melanoma or compromised immune systems due to medication.
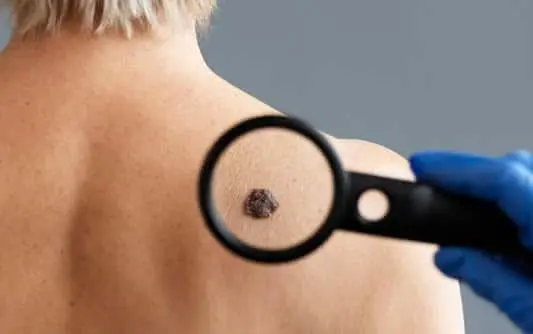
Another indication that it’s time to schedule a mole check-up is if a mole changes in appearance. New marks, discoloration, changes of shape or outline should be checked by a professional. These are potential signs of a malignant melanoma and will require a mole assessment and possible biopsy. Catching a melanoma early offers the best prospects. In this early stage the melanoma can be surgically removed to prevent further spread.
It’s important to remember that not all moles are found in visible locations – the back, for example. Individuals, particularly those with a lot of moles, may have moles that they cannot see – even in the mirror. These moles are much harder to monitor, and it is advisable for these individuals to schedule a periodic mole screening with a professional.
Identifying Dangerous Moles
The ABCDE protocol is designed to help detect possible melanoma. Healthy moles should appear symmetrical in shape, of uniform colour, with smooth edges, and a diameter of 6mm or less. Any mole that lies outside of these parameters should be checked by a Dermatologist who will assess whether or not biopsy is required.
A biopsy involves the surgical removal of a suspicious mole for examination. By conducting a biopsy, the Dermatologist will be able to assess whether or not the pigmented lesion is cancerous and, if so, whether the melanoma has spread to the lymph glands (sentinel node biopsy).
The regular checking of moles on your body is fundamental to maintaining skin health and preventing the spread of melanoma. As well as checking your moles at home once a month, it’s important to reach out to a professional if you notice a suspicious mole or pigmented lesion.
Schedule a appointment today with Dermatologist in Chatsworth.